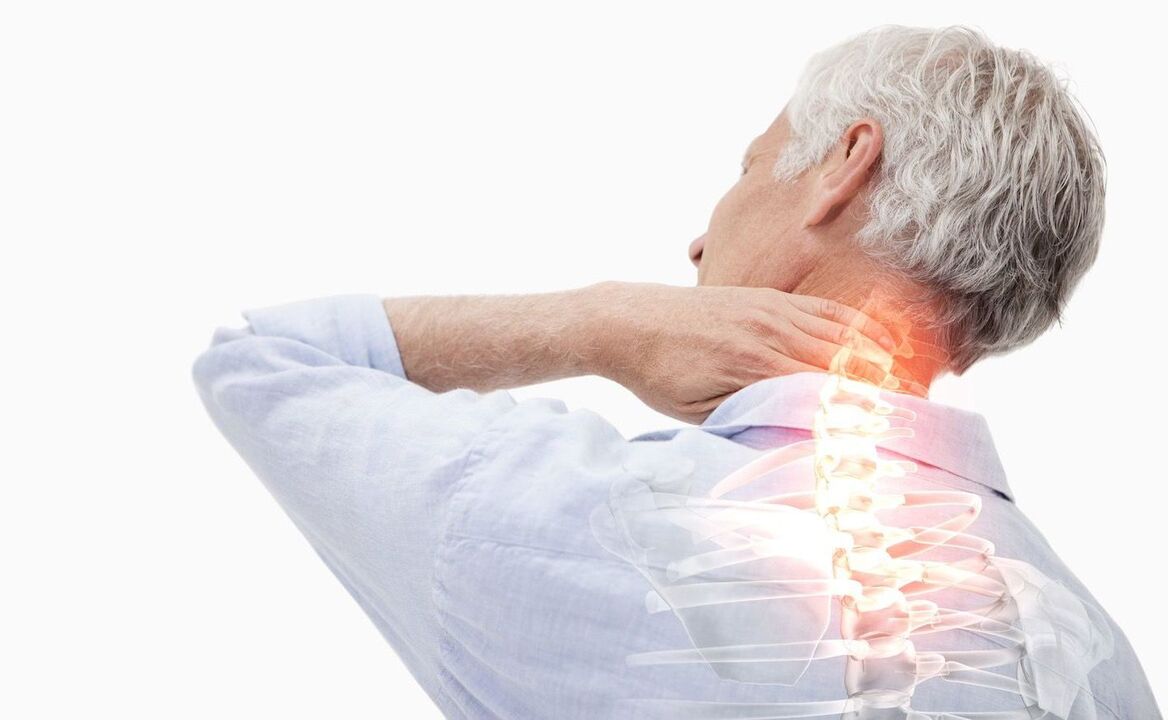
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
- Narrowing of the spinal canal in certain areas of the spine.
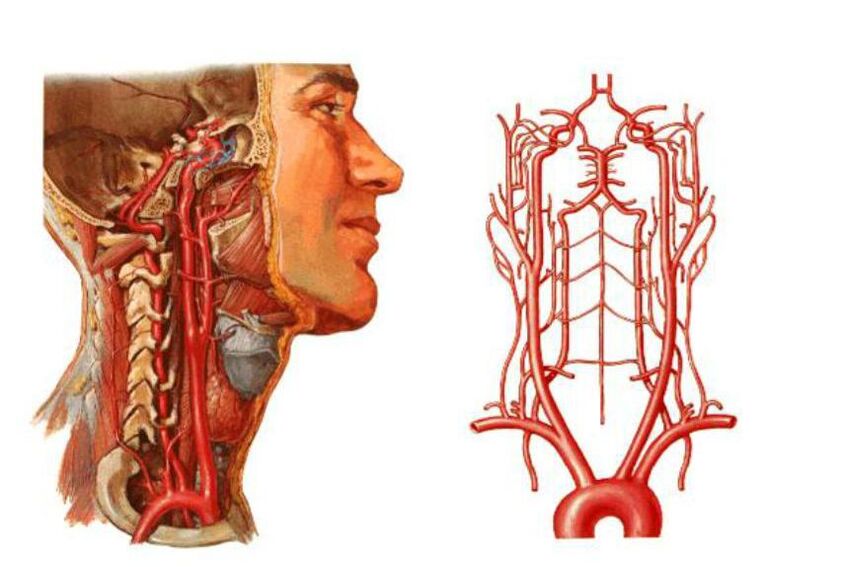
- Compression of the vertebral arteries - the large blood vessels that provide blood supply to the brain. As a result, the supply to the brain deteriorates and blood circulation in the cervical spinal cord is disturbed.
- The discs may become deformed and flatten. This can lead to compression of certain areas of the spinal cord and nerves, most commonly compression of the nerve roots.
- M02—Intervertebral disc dystrophy in adolescence.
- M42. 12 – Degenerative processes in the adult neck.
reason
- Pathological - under the influence of external adverse factors, the intervertebral disc and other vertebral body structures are destroyed, and the pathological process involves nearby tissues, blood vessels, and nerve bundles. The more severe these factors and other pathologies are, the faster the disease develops.
- Physiology-The development of pathology is mainly based on age-related changes. We are talking about the natural aging of the cartilage tissue of the spine, salt deposition, etc.
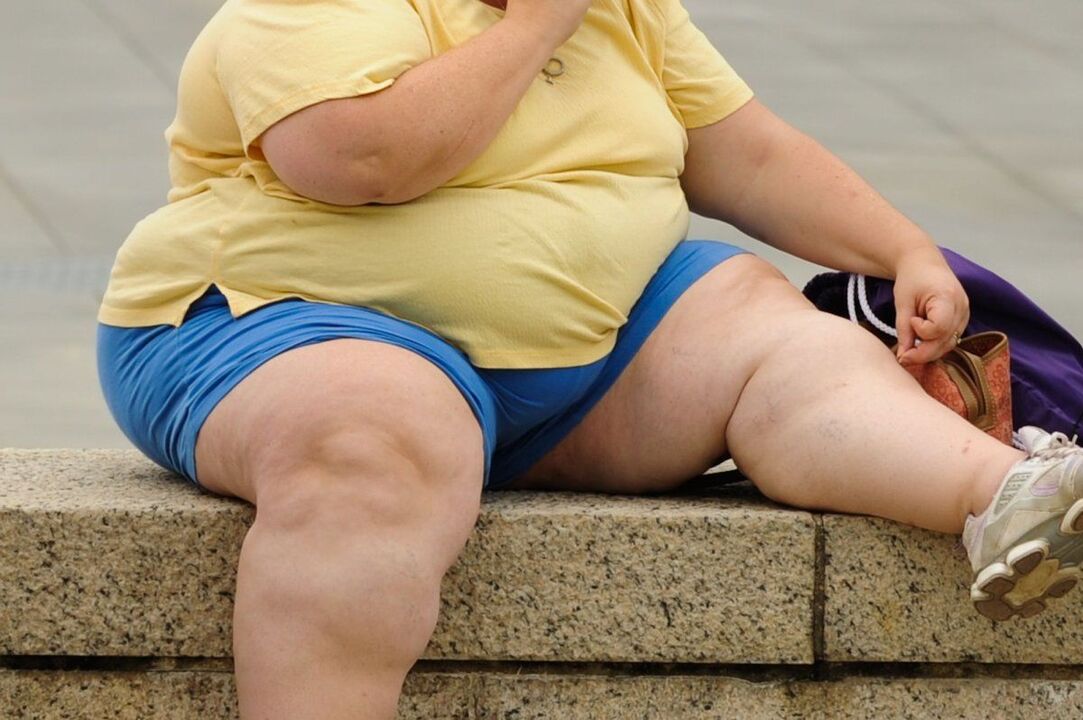
- Disturbances of metabolic processes in the body, as well as certain stages of obesity.
- Physical inactivity is a phenomenon characterized by limited mobility. We’re not just talking about injuries or illnesses, this includes sedentary lifestyles and sedentary jobs.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system lead to impaired blood circulation in the brain, changes in pressure, etc.
- Improper posture includes various forms of scoliosis, rheumatism and even flat feet.
- Cervical spine injury. In this case, we're talking about sprains, blows, bruises. Injuries elsewhere in the spine can influence the development of cervical osteochondrosis.
- Excessive physical stress on the cervical spine due to strenuous exercise or severe physical difficulty, depending on the person's type of activity.
- A sedentary lifestyle is also dangerous because if you sit incorrectly or on uncomfortable furniture, you can put constant strain on your cervical vertebrae and entire spine.
- Cervical hernia and various accompanying diseases.
- Forcing the head to remain in an uncomfortable or unnatural position for an extended period of time. In this case, not only does muscle strain occur, but it can also lead to curvature of the spine in the neck.
- Doctors believe that ongoing stress and nervousness are a very common cause.
- One of the causes is also thought to be congenital abnormalities of the spinal structure.

What harm does it have to health?
- Osteochondrosis is associated with spinal deformities that cause the spinal canal to narrow in certain areas. This can cause compression of the spinal cord and nerve branches, leading to serious neurological problems. In severe cases, the person may experience pain and may even lose control of certain parts of the body (mainly the arms or face).
- As already mentioned, compression of blood vessels in the neck can lead to impaired blood circulation in the occipital region of the brain. In this condition, the brain stops receiving the required amounts of oxygen and nutrients and becomes deprived of oxygen. If circulation is compromised, there is a real risk of ischemic stroke and various neuropathologies.
syndrome
- spine.
- Vertebral artery.
- Koreshkovi.
- heart.
spinal syndrome
- Partial or complete restriction of neck movement.
- Head movements are accompanied by a feeling of pain in the neck.
- X-rays show morphological changes in tissues (intervertebral and vertebral bodies).
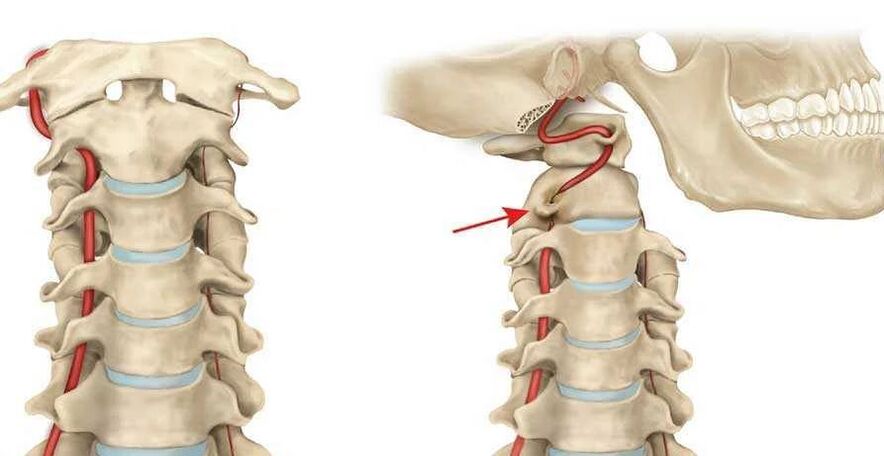
vertebral artery syndrome
- Headaches and migraines.
- Visual impairment.
- There is noise in the ears.
- Frequent dizziness, etc.
radiculopathy syndrome
- 1 pair - numbness or pain in the back of the head;
- The third pair - impaired chewing reflex, numbness of the tongue, unpleasant sensation behind the ears;
- 4 pairs - pain in the clavicle area and impaired swallowing reflex;
- 5 pairs - shoulder girdle disease with arm movement problems;
- Couple 6 - The patient begins to experience pain and numbness in the forearm and shoulder blade;
- Seventh pair - the hands and fingers (usually the index and middle fingers) become numb;
- Pair 8 – Similar problem to the previous point, but the ring and pinky fingers feel numb.
cardiac syndrome
- Rapid pulse.
- Sternal pain.
- Shortness of breath, weakness, lethargy, decreased performance.
disease progression
- The first stage is characterized by unclear symptoms. The patient complained of a mild headache; during initial examination, the physician noted mild muscle stiffness.
- Pain in the cervical spine and head is more common, more severe, and radiates to the shoulders and arms. The pathology results from disc damage and nerve root compression. The pain worsens when you turn your head, lean back, and bend forward.
- In the third stage, the pain persists, the arm muscles weaken, and the discs herniate. Neck movement is limited and dizziness often occurs.
- The fourth stage is accompanied by complete destruction of the disc, with cartilage tissue being replaced by connective tissue. In addition to pain and dizziness, coordination problems are observed, and the vertebral arteries are often compressed.
Signs and symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
- The pain of osteochondrosis is always present, but varies in intensity and frequency. Pain is the first clinical symptom. Their intensity depends on the stage of disease progression; they are blunt or compressive in nature. Pain is felt primarily in the neck and occipital areas, but can also radiate to the temporal areas, shoulder girdle, and arms.
- In most cases, there will be vestibular organ damage. We're talking about frequent unexplained dizziness, nausea, poor movement coordination, unbalanced gait, and loss of space.
- One of the most common clinical symptoms is neck muscle stiffness and stiffness of movement. A person has difficulty turning, lowering and tilting his head back, and the movements are accompanied by pain.
- Many patients report a "goosebumps" feeling or a characteristic tingling sensation on the scalp.
- Muscle weakness and numbness in the arm area.
- There are often psychological manifestations, including depression, lethargy, sudden changes in mood, bad temper, or irritability.
- Due to poor circulation and damage to brain tissue, dizziness worsens and noises in the ears that resemble rustling, pulsing and ringing occur.
- Most patients notice decreased vision, as well as pain in the eyeball, especially when trying to squint too much to the left, right, up, or down.
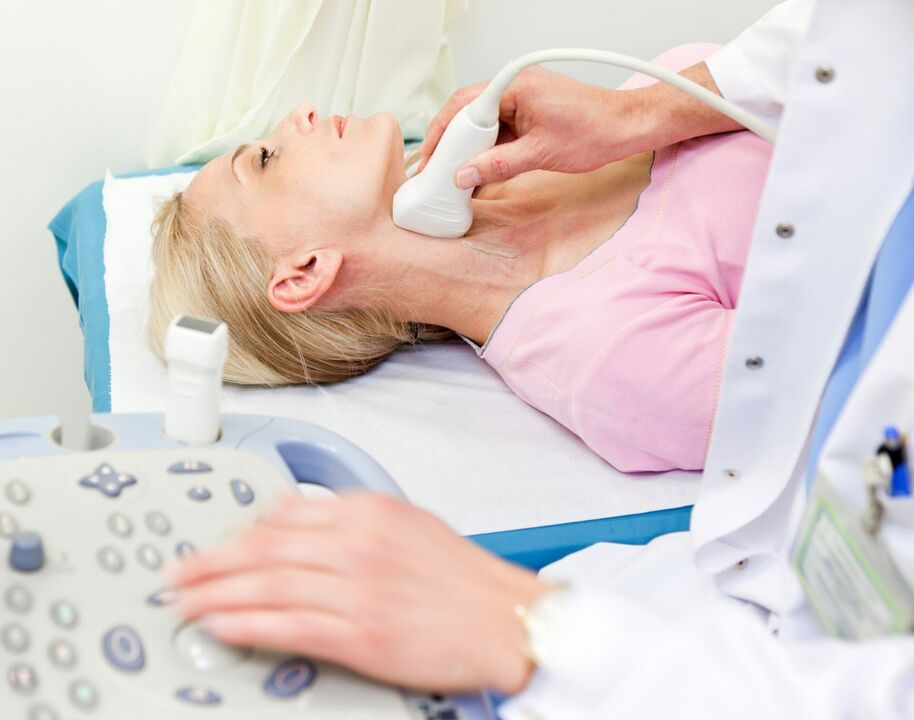
diagnosis method
- X-ray examination is the main method to determine the degree and position of spinal deformity.
- Computed tomography can more accurately diagnose pathological changes in the vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) – allows a detailed examination of the discs and vertebrae to determine the presence of hernias, herniations, extent of disease, etc.
- Dopplerography - With this test, it is possible to find where the arteries are compressed and to assess the extent of the circulatory disorder.
treatment method
medical treatement
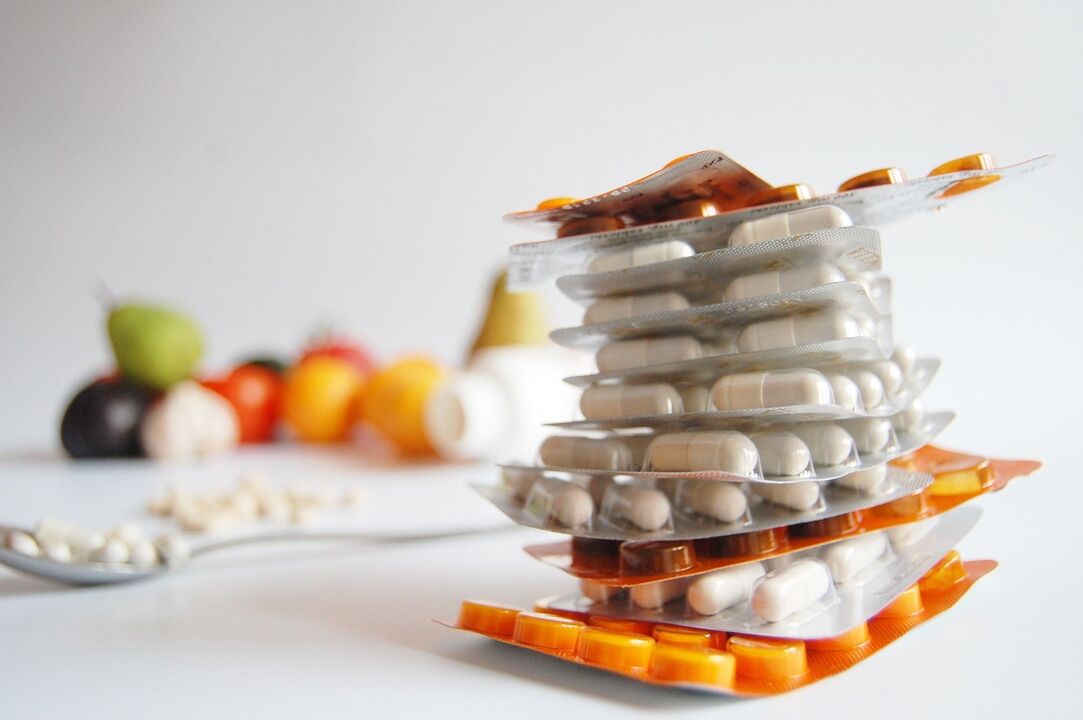

- Painkillers - Analgesics and antispasmodics. The first directly paralyzes nerve centers, thereby reducing pain sensations. The latter can relieve neck muscle spasms, improve blood flow and suppress pain.
- NSAIDs - Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are necessary to reduce inflammation and most also eliminate pain. These medications usually come in the form of a gel or ointment that is applied to the affected area.
- Muscle relaxants are another way to relieve neck muscle spasms.
- In certain stages of spinal osteochondrosis, chondroprotectants are necessary as they aid in the recovery of bone tissue.
- B vitamins—normalize the metabolic processes of nervous tissue, improve the conductivity of nerve impulses, and promote the function of the central nervous system.
physiotherapy
- Electrophoresis.
- Laser Treatment.
- ultrasound.
- massage.
physiotherapy
manual therapy
Kuznetsov applicator
treatment at home
- To use horseradish, take a leaf of this plant, pour boiling water over it and apply the inside to your neck, securing it with a bandage. Can continue to be used while sleeping for enhanced effects.
- If there are no contraindications from your doctor, cervical spine warming can be a good treatment. The easiest way is to use pepper paste, but you can heat the wax cake and apply it 1-2 times until completely cooled.
prevent disease
- Sleep on a flat, hard surface; it's best to invest in a special orthopedic mattress and pillow that fits the shape of your head.
- To prevent this disease, monitor your physical activity and do not overstrain the spine. If you must lift weights, do so smoothly and keep your back straight.
- If your job requires you to sit for long periods of time, take breaks. Every hour you need to walk or stretch out stiff muscles with simple gymnastic movements.